Remote Procedure Call
Trong khi lập trình ứng dụng, có những ứng dụng được xây dựng thành nhiều tiến trình khác nhau, chạy đồng thời. Các tiến trình này có thể hoạt động trên cùng một hệ thống, hoặc hoạt động trên nhiều hệ thống khác nhau. Các tiến trình này trao đổi dữ liệu qua lại với nhau, quá trình này gọi là Interprocess Communications (IPC). Remote Procedure Call (RPC) là một phương pháp dùng để trao đổi dữ liệu. RPC khiến cho việc thực hiện IPC dễ dàng, giống như một lời gọi hàm bình thường. RPC có thể được thực hiện giữa hai tiến triền trên cùng một máy tính, hoặc giữa các máy tính khác nhau trong mạng.
Microsoft Windows API cung cấp cơ chế RPC tuân theo Open Software Foundation (OSF) Distributed Computing Environment (DCE). Có nghĩa là, bất kì ứng dụng nào sử dụng RPC dựa vào Windows API, hoàn toàn có thể trao đổi với ứng dụng khác sử dụng RPC theo chuẩn DCE.
Thuật ngữ:
- interface: Giao diện mô tả cách thức giao tiếp của RPC. RPC sử dụng một ngôn ngữ đặc biệt để mô tả interface, đó là Interface Definition Language (IDL). IDL của Microsoft là Microsoft Interface Definition Language (MIDL).
- Remote Procedure : là các hàm được xây dựng tuân theo interface định nghĩa trước.
- Client: là chương trình sử dụng RPC để thực hiện một nhiệm vụ.
- Server là chương trình nhận các yêu cầu từ client, thực hiện nhiệm vụ định trước, trả lời kết quả cho client.
Các thành phần chính của Microsoft RPC:
- Trình biên dịch MIDL (MIDL compiler)
- Các thư viện liên kết động (Rpcrt4.dll)
- Name service provider
- Endpoint mapper
Microsoft Interface Definition Language (MIDL)
Đây là ngôn ngữ mô tả interface được Microsoft sử dụng. Viết một file IDL cũng tương tự như khi định nghĩa header trong ngôn ngữ C, nhưng bản thân ngôn ngữ này có thêm một vài keyword khác biệt. IDL tập trung mô tả thuộc tính của hàm và các tham số của hàm. Sau khi mô tả IDL xong, nó cần được dịch thành các file .c và .h thông qua MIDL compiler.
Để dễ hiểu, tôi sẽ bắt đầu bằng một ví dụ:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_BUFF (256)
void SayYouDo( __in const char *s)
{
printf("%s", s);
}
void main(void)
{
char buf[MAX_BUFF];
printf("Enter a string and press [ENTER]. Enter QUIT to exit.\n");
do
{
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
if (fgets(buf, 256, stdin)== NULL)
break;
SayYouDo(buf);
} while (strcmp(buf, "QUIT\n"));
}
Logic của chương trình này rất đơn giản:
- Đợi người dùng nhập dữ liệu, hiển thị nó ra màn hình.
- Nếu người dùng nhập QUIT, thì hiển thị QUIT và thoát.
Câu hỏi đặt ra là nếu viết lại chương trình này, thay lời gọi hàm SayYouDo() thành RPC thì sẽ thế nào?
Xây dựng file IDL
// File SayYouDo.idl
// Compiling SayYouDo.idl:
// midl /app_config SayYouDo.idl
[
// interface unique identifier.
uuid(B0ACC031-03B0-45de-8751-D205210BA42D),
// Version 1.0 of this interface.
version(1.0),
// This interface will use an implicit binding
implicit_handle(handle_t hBinding)
]
interface RpcExample
{
void SayYouDo(
[in, string] const char* s // a zero-terminated string.
);
void ShutdownRpc( void );
}
Mô tả trên bao gồm:
UUID: Các interface được phân biệt với nhau thông qua uuid. Giá trị này phải là duy nhất. UUID có thể sinh ra bằng công cụ Create UUID của Microsoft. Công cụ này có sẵn trong bộ Visual Studio.
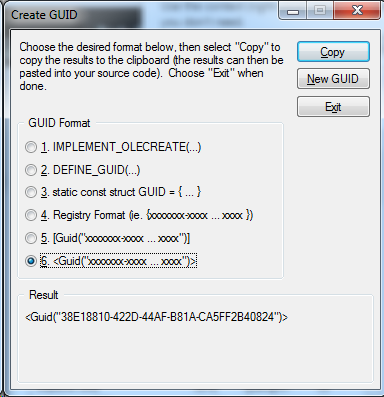
version: cho biết phiên bản của interface. Trong ví dụ này là 1.0
binding handle:
Để hiểu khái niệm này, cần hiểu Binding là một quá trình thiết lập một kết nối logic (logical connection) giữa chương trình client và chương trình server. Thông tin về kết nối nữa client và server được biểu diễn thông qua một cấu trúc, gọi là binding handle.
Trên thực tế, RPC client và RPC server có thể nằm trên cùng một máy tính hoặc trên 2 máy tính khác nhau. Client và server có thể giao tiếp thông qua nhiều loại giao thức khác nhau (TCP, Named pipe, ...). Về mặt logic, client và server chỉ hiểu là đang kết nối với nhau thông qua binding handle mà không cần hiểu nền tảng giao tiếp bên dưới (TCP, Named pipe, ...) đang dùng là gì. Tham khảo danh sách các Protocol có thể dùng được: Protocol Sequence.
Có 3 loại binding handle có thể dùng được, bao gồm: implicit_handle, auto_handle và explicit_handle.
- implicit_handle có nghĩa là binding handle được hiểu ngầm định, không cần phải có trong tham số khi gọi hàm RPC. Nên dùng loại này.
- explicit_handle có nghĩa là binding handle được hiểu tường minh, buộc phải có trong tham số khi gọi hàm RPC. Đây là tham số đầu tiên của hàm.
- auto_handle: có thể hiểu là kiểu kết hợp của 2 kiểu trên.
Biên dịch MIDL bằng MIDL compiler có sẵn của Visual Studio
tùy chọn /app_config cho phép sử dụng một số keyword của Application Configuration File (ACF) bên trong file IDL.
interface: Định nghĩa interface bao gồm tên hàm và các tham số. Các tham số cần định nghĩa rõ kiểu dữ liệu . Thuộc tính của các trường dữ liệu trong ngôn ngữ IDL có thể tham khảo ở đây: IDL Attributes
Compile MIDL file
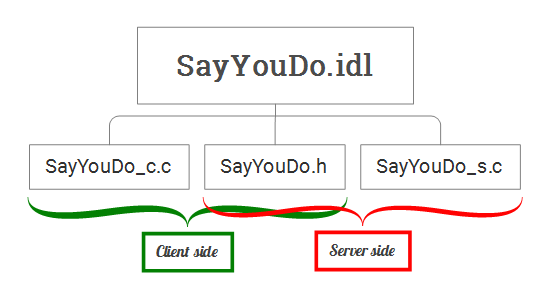
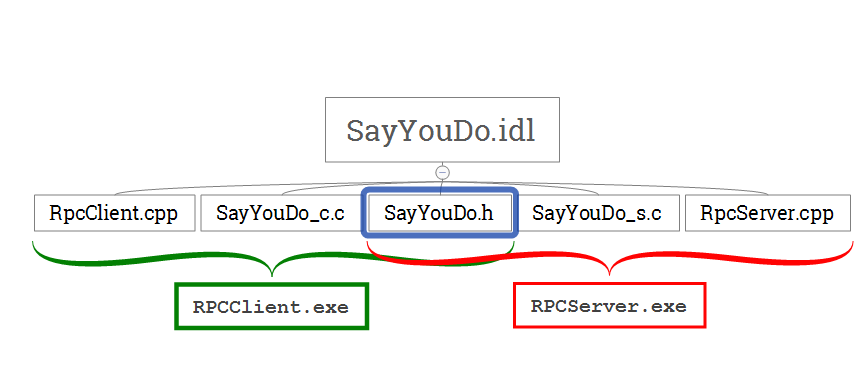
Sử dụng MIDL Compiler để sinh code cho client và server. Quá trình này sẽ tạo ra 3 file:
SayYouDo.h: Header cho cả client và server
SayYouDo_c.c: Client stub
SayYouDo_s.c: server stub
Trong quá trình biên dịch, cần lưu ý: chọn đúng nền tảng (x86, x64 hay ia64) khi biên dịch. Tham số này có thể tham khảo thông qua tùy chọn /win32, /x64 hoặc /ia64 của midl compiler.
RPC Server
#include <iostream>
#include "../Protocol/SayYouDo.h"
#pragma comment(lib, "Rpcrt4.lib") // RPC Functions
#if defined UNICODE || defined _UNICODE
#define RPC_TSTR RPC_WSTR
#else
#define RPC_TSTR RPC_CSTR
#endif
#define RPC_PROTOCOL TEXT("ncacn_np")
#define RPC_NETWORK_ADDRESS (NULL)
#define RPC_END_POINT TEXT("\pipe\hello")
HANDLE hStopEvent = NULL;
// Server functions.
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"{
#endif
void SayYouDo(const unsigned char *s)
{
std::cout << s;
}
void ShutdownRpc( void )
{
if (hStopEvent)
{
SetEvent(hStopEvent);
}
}
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
// Naive security callback.
RPC_STATUS CALLBACK SecurityCallback(RPC_IF_HANDLE /*hInterface*/, void* /*pBindingHandle*/)
{
return RPC_S_OK; // Always allow anyone.
}
int main( int argc, char *argv[])
{
RPC_STATUS status;
hStopEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, TRUE, FALSE, NULL);
if (hStopEvent == NULL)
return 0;
// Uses the protocol combined with the endpoint for receiving RPC.
std::cout << "Initializing RPC server ..." << std::endl;
status = RpcServerUseProtseqEp(
reinterpret_cast<RPC_TSTR>(RPC_PROTOCOL), // protocol.
RPC_C_PROTSEQ_MAX_REQS_DEFAULT, // Backlog queue .
reinterpret_cast<RPC_TSTR>(RPC_END_POINT), // endpoint.
NULL); // No security.
if (status)
exit(status);
std::cout << "Registering RPC server ..." << std::endl;
status = RpcServerRegisterIf2(
RpcExample_v1_0_s_ifspec, // Interface to register.
NULL,
NULL,
RPC_IF_ALLOW_CALLBACKS_WITH_NO_AUTH, // Forces use of security callback.
RPC_C_LISTEN_MAX_CALLS_DEFAULT, // Use default number of concurrent calls.
(unsigned)-1, // Infinite max size of incoming data blocks.
SecurityCallback); // Naive security callback.
if (status)
exit(status);
// Start to listen for RPC.
std::cout << "Listen RPC server ..." << std::endl;
status = RpcServerListen(
1, // Recommended minimum number of threads.
RPC_C_LISTEN_MAX_CALLS_DEFAULT, // Recommended maximum number of threads.
TRUE); //dont wait
// Start listening now. Wait for stop-message
WaitForSingleObject(hStopEvent, INFINITE);
Sleep(1000);
RpcMgmtStopServerListening(RpcExample_v1_0_s_ifspec);
RpcServerUnregisterIf(RpcExample_v1_0_s_ifspec, NULL, 0);
CloseHandle(hStopEvent);
std::cout << "Server stopped." << std::endl;
if (status)
exit(status);
return 0;
}
// Memory allocator
void* __RPC_USER midl_user_allocate(size_t size)
{
return malloc(size);
}
void __RPC_USER midl_user_free(void* p)
{
free(p);
}
Đăng kí interface
Chương trình sẽ đăng kí một interface với hệ thống thông qua hàm RpcServerRegisterIf2.
RPC_STATUS RPC_ENTRY RpcServerRegisterIf2( RPC_IF_HANDLE IfSpec, UUID *MgrTypeUuid, RPC_MGR_EPV *MgrEpv, unsigned int Flags, unsigned int MaxCalls, unsigned int MaxRpcSize, RPC_IF_CALLBACK_FN *IfCallbackFn );
Theo kinh nghiệm bản thân, các bạn nên dùng hàm RpcServerRegisterIf2 hoặc RpcServerRegisterIfEx thay cho RpcServerRegisterIf khi đăng kí interface. Nên thiết lập cờ RPC_IF_ALLOW_CALLBACKS_WITH_NO_AUTH khi đăng kí interface, IfCallbackFn thì có thể thiết lập hoặc đặt bằng NULL.
Điều này sẽ tránh cho client ( xin nhắc lại là client) bị crash giữa chừng khi kết nối tới RPC server. Lỗi này khá khó chịu! Client sẽ bị crash khi gọi hàm NdrClientCall2, trong lúc cố kết nối tới server. Các bạn sẽ không bao giờ dùng hàm NdrClientCall2 trong code của các bạn, NdrClientCall2 được sinh ra tự động trong client code stub.
RpcServerListen để bắt đàu nhận kết nối từ client. Sau hàm này, server có thể coi là sẵn sàng.
Implement interface
ở đây, mình implement cho 2 hàm SayYouDo và ShutdownRpc.
Phía server cần implement 2 hàm cho quản lý bộ nhớ:Hai hàm này được sử dụng khi hệ thống cấp phát bộ nhớ động khi chạy.
void* __RPC_USER midl_user_allocate(size_t size); void __RPC_USER midl_user_free(void* p);
Shutting down the server
Để tắt RPC server, bạn dùng hàm RpcMgmtStopServerListening. Để biết khi nào tắt server, thì có thể điều khiển qua client như mình làm.
RPC Client
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "../Protocol/SayYouDo.h"
#pragma comment(lib, "Rpcrt4.lib") // RPC Functions
#if defined UNICODE || defined _UNICODE
#define RPC_TSTR RPC_WSTR
#else
#define RPC_TSTR RPC_CSTR
#endif
#define RPC_PROTOCOL TEXT("ncacn_np")
#define RPC_NETWORK_ADDRESS (NULL)
#define RPC_END_POINT TEXT("\pipe\hello")
int main( int argc, char *argv[])
{
RPC_STATUS status;
RPC_TSTR szStringBinding = NULL;
// Creates a string binding handle.
status = RpcStringBindingCompose(
NULL, // UUID to bind to.
reinterpret_cast<RPC_TSTR>(RPC_PROTOCOL), // protocol.
reinterpret_cast<RPC_TSTR>(RPC_NETWORK_ADDRESS), // network address to use.
reinterpret_cast<RPC_TSTR>(RPC_END_POINT), // endpoint.
NULL, // Protocol dependent network options to use.
&szStringBinding); // String binding output.
if (status)
exit(status);
// Validates the format of the string binding handle
status = RpcBindingFromStringBinding(
szStringBinding, // The string binding to validate.
&hBinding); // Put the result in the implicit binding handle
if (status)
exit(status);
char buf[256];
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
bool bStopped = false;
std::cout << "Enter a string and press [ENTER]. Enter QUIT to exit." << std::endl;
do
{
fgets(buf, 256, stdin);
bStopped = (strcmp(buf, "QUIT\n") == 0);
RpcTryExcept
{
SayYouDo((const unsigned char *)buf);
}
RpcExcept(1)
{
std::cerr << "Exception " << RpcExceptionCode() << std::endl;
bStopped = true;
break;
}
RpcEndExcept
} while (!bStopped);
// send shutdown signal
RpcTryExcept
{
// Calls the RPC function.
ShutdownRpc();
}
RpcExcept(1)
{
std::cerr << "Exception " << RpcExceptionCode() << std::endl;
}
RpcEndExcept
// Free the memory allocated by a string.
status = RpcStringFree(
&szStringBinding); // String to be freed.
if (status)
exit(status);
// Releases binding handle
status = RpcBindingFree(
&hBinding); // Frees the implicit binding handle
if (status)
exit(status);
return 0;
}
// Memory allocator
void* __RPC_USER midl_user_allocate(size_t size)
{
return malloc(size);
}
void __RPC_USER midl_user_free(void* p)
{
free(p);
}
Client sử dụng RpcStringBindingCompose để tạo binding string và chuyển đổi string thành binding handle thông qua hàm RpcBindingFromStringBinding
Client cũng cần 2 hàm cho việc quản lý bộ nhớ động, như ở server.
Sau khi tạo handle thành công, client sẽ gọi hàm thông qua RPC như sau:
RpcTryExcept
{
SayYouDo((const unsigned char *)buf);
}
RpcExcept(1)
{
std::cerr << "Exception " << RpcExceptionCode() << std::endl;
}
RpcEndExcept
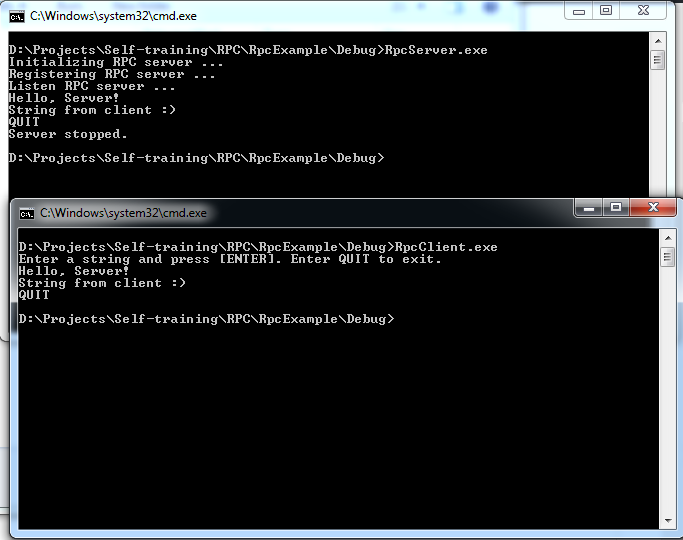
Compile and Link
Lưu ý khi dùng explicit_handle
Trong trường hợp dùng explicit_handle thì cần khai báo như sau:
// File SayYouDo.idl
// Compiling SayYouDo.idl:
// midl /app_config SayYouDo.idl
[
// interface unique identifier.
uuid(B0ACC031-03B0-45de-8751-D205210BA42D),
// Version 1.0 of this interface.
version(1.0),
explicit_handle
]
interface RpcExample
{
void SayYouDo(
[in] handle_t hBinding,
[in, string] const char* s // a zero-terminated string.
);
void ShutdownRpc( [in] handle_t hBinding );
}
Server :
// Server functions.
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"{
#endif
void SayYouDo(handle_t hBinding, const unsigned char *s)
{
std::cout << s;
}
void ShutdownRpc( handle_t hBinding)
{
if (hStopEvent)
{
SetEvent(hStopEvent);
}
}
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
Client
// Validates the format of the string binding handle
status = RpcBindingFromStringBinding(
szStringBinding, // The string binding to validate.
&hBinding); // Put the result in the implicit binding handle
if (status)
exit(status);
RpcTryExcept
{
SayYouDo(hBinding, (const unsigned char *)buf);
}
RpcExcept(1)
{
std::cerr << "Exception " << RpcExceptionCode() << std::endl;
}
RpcEndExcept
Source Code - Mã nguồn
Đây là toàn bộ mã nguồn chương trình mẫu: RpcExample.
Nếu có câu hỏi, các bạn vui lòng để lại comment bên dưới, mình sẽ trả lời.
